Expanding the capabilities of wearable devices with GNSS – a Taiwanese case study

The article explores the product line of the wearables industry and analyses the ways it benefits from GNSS-powered innovative solutions and applications
Taiwan’s diverse wearable’s market
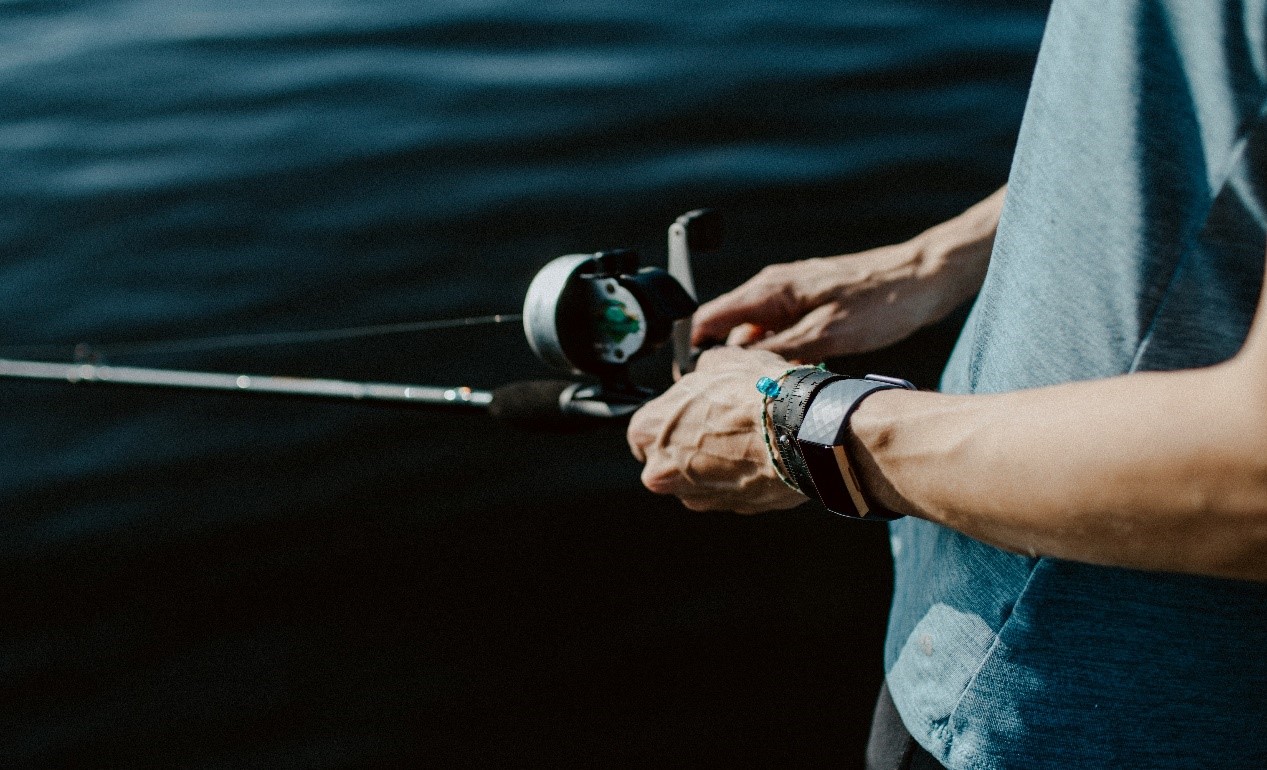
Thanks to its strong domestic ICT industry, Taiwan plays an important role in the global wearable device market. The country boasts multiple companies responsible for the development of wearable technologies, ranging from electronic components or complete solutions in image transmission to various consumer products. The most common wearable devices in Taiwan are smartwatches, smart glasses, smart fabrics, and tracking bracelets. Most wearables focus on sport and entertainment purposes, but medical wearable devices are also gaining more traction due to the increasing demand from Taiwan’s ageing society.
Leveraging the expertise to boost innovation
Taiwan’s globally competitive IT industry is the most important sector for the wearable device market. With its extensive OEM/ODM experience, complete supply chain, and R&D capabilities, it holds a dominant position on the world market. For example, LOCOSYS Technology provides OEM/ODM services from both hardware and software in GNSS and Wireless Communication to Embedded System and Consumers electronics, including GPS watches and loggers. RiTdisplay Corporation built several PMOLED lines for the production of mini panels for smartwatches, sport bands, and heartbeat detectors. Taiwan’s well-known textiles industry is another important sector for wearables. An example of a textile-based innovation is the rise of smart cloth -textile material with wearable devices embedded into the material itself. Large textile producers have adopted the new technology over the last few years, with companies such as AIQ Smart Clothing Inc focusing on a washable smart cloth with inbuilt heart rate monitors.
The rise of smart glasses
It is not only smart textiles that are seeing innovation – smart glasses are also on the rise. One key player in the smart glasses market is Jorjin – a company whose glasses utilise wireless networks including GNSS for use in VR/MR applications in manufacturing, power facility inspections, building maintenance, logistics and warehousing, as well as Emergency Medical Service Systems. In terms of industrial applications, China Steel Corp. and Formosa Plastics have applied smart glasses solutions provided by Jorjin and the Institute for Information Technology (III). The glasses are integrated into safety helmets and are used by operators for factory inspections and remote maintenance guidance. Through AR smart glasses, Formosa Plastics can display machine parameters in real-time at fixed points during inspections. Formosa also uses dynamic object tracking technology to allow smart glasses to automatically locate and mark objects within the user’s line of sight. The overlay is displayed in the correct position thereby providing a clear guidance message. with GPS/GLONASS for vehicles, people, and pets (iCar, iCare, and iPet), which provide geofencing, real-time location data, and location sharing functions, as well as the ability to send alerts to smartphones.
Joining the ranks of everyday devices
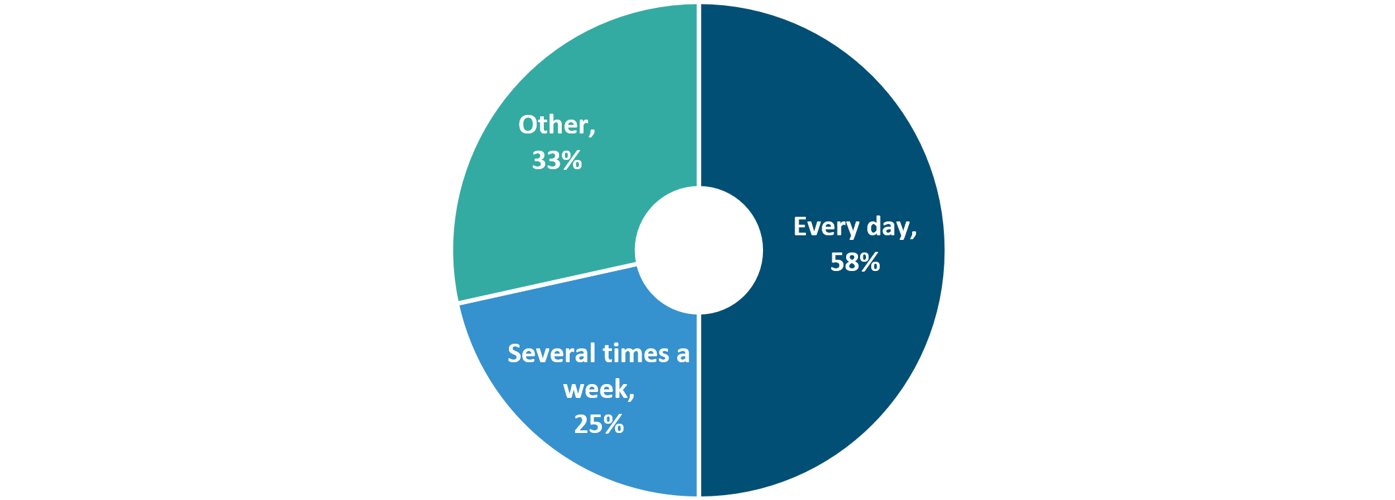
According to a survey by Rakuten Insight on wearable technologies, around 58% of respondents in Taiwan who owned a smart wearable stated that they used their smartwatch or fitness tracker every day. Around 25% of interviewees claimed that they used their smart wearable several times a week. More and more wearable GNSS devices, including smartwatches from Acer and ASUS, are designed to be multifunctional. They perform not only as sports trackers but contain a host of healthcare management functions, such as tracking sleep, monitoring heart rate, and counting steps, as well as allowing the user to answer text messages and phone calls.
The market-ready products
Other smartwatches are branching out from the typical tasks, with ASUS launching VivoWatch – a smartwatch – featuring a built-in, one-to-many remote cloud health management technology in conjunction with the Taoyuan Hospital and the Ministry of Health and Welfare. This technology is capable of remotely monitoring the physiology of suspected cases 24 hours a day to minimise the direct contact that medical staff are exposed to and, thus, greatly reducing the risk of infection. Local bank and insurance companies also launched financial products with fitness wearable applications to encourage customers to maintain a healthy lifestyle.