One year of success for QZSS (Michibiki) in Japan

This article analyses the results of the first year of operation of the Japanese satellite constellation and suggests potential takeaways for the European GNSS industry
According to a recent survey launched by QBIC (QZSS Business Innovation Council), the Japanese GNSS constellation QZSS (Quasi-Zenith Satellite System), aka “Michibiki”, run and operated by the Japanese government, is performing well since officially going live with the 4-satellite constellation in November 2018. It should be noted that the uptake of Michibiki is highest in B2B professional market segments, such as construction, surveying, agriculture, and other B2B sectors.
Between Michibiki’s launch in 2011 and 2015, nearly 150 application demonstrations have been arranged by SPAC (Satellite Positioning Research and Application Center). These were organised to showcase the potential of Michibiki’s high accuracy augmentation services by providing the prototypes of SLAS and CLAS for the private sector in various user segments, as well as academia. As part of this initiative, prototypes receivers – with software not available in the market at the time – were provided as part of this initiative. Since 2015, QSS Inc. (Quasi-zenith Satellite system Services Inc.) has joined SPAC’s demonstration as a co-coordinator. These demonstrations, so far, seem to contribute to the remarkable uptake of Michibiki’s services.
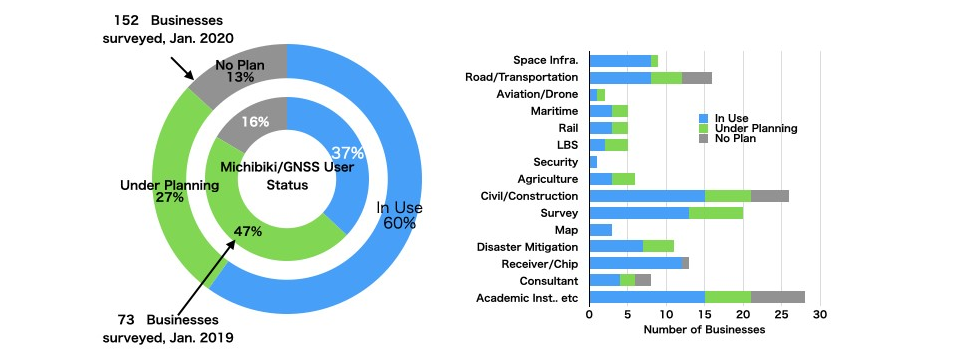
The survey shows how Michibiki has penetrated the Japanese market after one year of official operation and what are the key issues for the future of the constellation.
Key findings are summarized as follows:
- Michibiki is heading to a good start: The uptake of Michibiki by business users has dramatically increased from 37% to 60% in 2019. Meanwhile, still 13% of business respondents have no plan to use the constellation. Firms seem to wait for a better business environment and expect future service improvements with the completion of the 7-satellite full constellation in 2023.
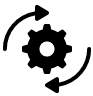
- The uptake of Michibiki begins in the B2B professional market segments such as Surveying, Construction, Mapping, and Agriculture which require high accuracy positioning: Meanwhile, uptake is lower in Consumer Solutions and Disaster Prevention/Mitigation. Future smartphones equipped with Michibiki’s unique services such as short messaging functions could be the key to the activation of these segments.
- All Michibiki Unique services are gaining ground: High accuracy services including Centimeter and Sub-meter accuracy as well as all Michibiki Unique Services are facing increasing demand. Nevertheless, the number of businesses using commercial RTK-GNSS solutions is still larger, partly because Michibiki performance is not yet as competitive in terms of accuracy and stability.
- The key to stronger Michibiki penetration is the provision of lower-cost receivers of Michibiki unique services: The market calls for lower-cost receivers with higher accuracy and stability, while free, attractive, and highly reliable services will spur industry penetration. Japan has taken the initiative to launch discussions at the ICG (International Committee of GNSS) on the interoperability of short messaging for disaster warning and high accuracy services (GNSS-PPP). This is expected to bring down the price of the specialised Michibiki receivers.
- Service reliability is the No.1 priority for business applications: For Michibiki users, service reliability is the first prioritised requirement followed by accuracy and stability. Future GNSS services are expected to offer improvements in anti-jamming measures as well as signal authentication and resilience. The latter is expected to be launched in 2023 and might be the key to driving penetration in the business segment.
The survey’s results also raise a number of relevant conclusions for European stakeholders, namely:
- Application Demonstrations bring good chances of early penetration to society for unique Galileo Services: Galileo is planning to start its High Accuracy Service as well as Signal Authentication Service in the future. SPAC’s experiences with Michibiki have shown that early demonstrations of these services in the EU, but also in Japan, could act as a great tool to promote the Galileo system and its differentiators.
- Smartphones equipped with Michibiki unique services such as SLAS, CLAS, MADOCA, as well as the Short Messaging functions could be the key to the activation of LBS market segments: Michibiki in Japan seems to have not been adopted by mass-market users as of yet. Therefore, EU industries still have many chances in Japan and the Asia-Oceania region by introducing such handsets and receivers. The European Commission and Japan are discussing the interoperability between Galileo and Michibiki in terms of High-Accuracy Services and Short Messaging for disaster warnings, which may drastically lower the prices of receivers dedicated to Michibiki.
By 2023 Michibiki will expand its constellation from four to seven satellites, ensuring independent satellite positioning and improved performance with wider coverage of the Asia Pacific region. Discussions have now started on the Roadmap for Michibiki beyond 2023.